Steel structure roof trusses manufacturing process
- 22 Aug 2019
- steel structure
1. Construction preparation
1.1 Materials and main equipment and tools:
1.1.1 Steel: Q235 steel or 16 manganese steel shall be used according to the design drawings. The steel shall have a quality certificate and shall meet the design requirements and the current national standards.
1.1.2 Connecting materials: The connecting materials such as welding rods and bolts shall have quality certificates and meet the design requirements. Welding rods with peeling off or rusted cores,and the high-strength bolts with rust, bumps or mixed batches shall not be used.
1.1.3 Coatings: Anti-corrosion paints should meet the design requirements and relevant standards, and should have product quality certificates and instructions for use.
1.1.4 Main equipment and tools: shearing machine, steel straightening machine, steel plate flattening machine, drilling machine, electric drill, reaming drill; electric welding, gas welding, arc gouging equipment; steel plate platform; sand blasting, painting equipment, etc.
Tools: steel ruler, square ruler, caliper, stylus, scribe gauge, sledgehammer, chisel, sample punch, crowbar, wrench, straightener, clamp, drill, jack, etc.
2. Working conditions:
2.1 Before the production of the steel structure roof truss, draw the detailed construction drawings of the steel structure according to the design documents provided by the design company. When the drawings are revised, they should go through the negotiation formalities with the design company.
2.2 Prepare manufacturing process documents (process specifications) in accordance with the requirements of the design documents and construction detailed drawing.
2.3 The accuracy of steel ruler used for production, installation, inspection and acceptance should be consistent and verified by the statutory measurement and testing department.
3.Operating process
3.1 Manufacturing process:
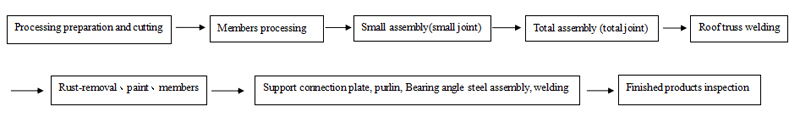
3.2 Processing preparation and cutting:
3.2.1 Laying-off: Laying-off according to the construction drawing, the welding shrinkage and machining allowance should be reserved when laying-off and number the material. After it was approved by the inspection personnel, they will go through the pre-inspection procedures.
3.2.2 Making the sample according to the laying-off (sample rod).
3.2.3 Steel correction: Before the material is cut, the steel must be corrected. The deviation value after correction should not exceed the allowable deviation value specified in the specification to ensure the quality of the material.
3.2.4 When the steel structure roof truss is placed on the upper and lower strings, the holes are not numbered, and the remaining parts are all numbered; the hot-rolled steel is hot-processed, and the holes are numbered when it is cooled.
3.3 Parts processing:
3.3.1 Cutting: The rust and pollution in the steel cutting area before oxygen cutting should be cleaned up. After the cutting, the fracture margin tumor and the spatter should be removed. The mechanical shear surface shall be free from cracks and defects greater than 1 mm, and the burrs shall be removed.
3.3.2 Welding: When the upper and lower string steels need to be connected, the joint head is welded and straightened firstly. When the steel joint is used, in order to make the joint steel and the rod steel closely attached, the corners should be shoveled as designed. Butt welds shall be welded to the ends of the welded joints with run-on plate. The material and the groove type shall be the same as the weldments, and the gas cuts shall be cut and smoothed after welding.
3.3.3 Drilling; bolts for the base plate of the end of the roof truss are drilled by steel die, and can be drilled by general scribing method.
3.3.4 Small assembly (small joint); the T-shaped base of the roof truss end and the window frame support plate are pre-welded and formed the components, and then assembled to the roof truss after correction. In order to prevent deformation of welding parts, it is advisable to use a pair of back-to-backs, clamped with a clamp and then welded.
3.4 total assembly (total joint):
3.4.1 Place the actual sample on the assembly table, arch according to the construction drawing and process requirements and reserve the amount of welding shrinkage. The assembly platform should have a certain rigidity, and deformation should not occur, which affects the assembly precision.
3.4.2 According to the actual sample, the positioning angles such as the upper string, the lower string and the web are lap welded on the assembly table.
3.4.3 Place the upper and lower chord plates and the node connecting plate on the actual sample, and place the pair on the seat, then place the upper and lower chords on the connection plate so that they are close to the positioning angle. After the half-piece truss members are all placed and confirmed according to the construction drawings, then the spot welding can be positioned.
3.4.4 The spot-welded half-slab truss is flipped 180 , and the half-piece truss is used as a molded to replicate the assembly roof truss.
3.4.5 Place the pad, the connecting plate and the base plate on the half-slab truss. The base plate and the center vertical rod of the roof louver support is bolted to the positioning plate with holes to ensure the accuracy of the component size.
3.4.6 Place the upper and lower chords and the webs on the connecting plate and the pad, clamp them with clamps, and perform spot welding.
3.4.7 Flip the half-piece truss on the mold tire by 180 , then place the other surface of the upper and lower chord and the web on the connecting plate and the pad, so that the steel back is aligned with the clamp and clamped. Then Carrying our the spot welding, the entire assembly of the truss is completed when the fire is over, and the assembly of the other trusses is repeated in the above order.
3.5 Steel structure roof truss welding:
3.5.1 The welder must have a network certificate. Arrange the welding work of the welder to be compatible with the technical level of them.
3.5.2 The assembly quality and the treatment of the weld zone should be reviewed before welding. Only after the repair, the weld can be applied.
3.5.3 Welding sequence: first welding the side of the upper and lower chords, and then weld the pad between upper and lower chords. One side of the roof truss is fully welded and then inverted, and the other side is welded. The welding sequence is the same.
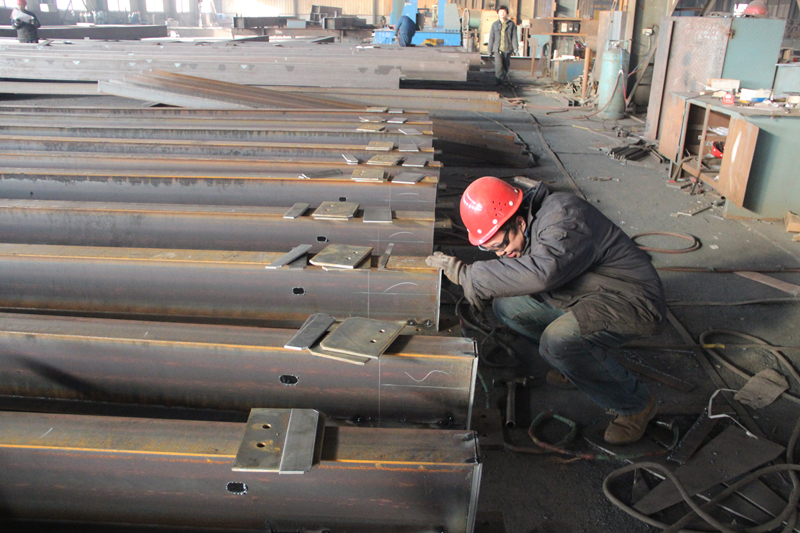

3.6 Assembling and welding of the supporting connecting plate, and the purlin support angle steel; using the sample rod to draw out the position of the supporting connecting plate, aligning the supporting connecting plate with the position and positioning the spot welding. Use the sample rod to draw the angle steel position as well, and level the weld seam at the assembly, place the purlin angle bracket on the assembly position and position the spot weld. After all the assembly is completed, the welding of the purlin support angle steel is started, and then the connecting plate. After the welding, the slag splash should be removed. Mark the welder code on the welds and parts as specified in the manufacturing process.
3.7 finished product inspection:
3.7.1 The welding is completed, and after the weld is cooled for 24 hours, all the inspections are made and recorded. I and II welds shall be ultrasonically flawed.
3.7.2 When connecting with high-strength bolts, the friction surface of the components shall be sandblasted and six sets of pieces test shall be made. Three of them shall be sent to the installation site when they are shipped from the factory for re-testing friction coefficient.
3.7.3 According to the construction drawing requirements and construction specifications, check and accept the geometric shape of the finished product, and record the every roof truss.
3.8 Rust removal, paint, numbering.
3.8.1 Rust removal after the finished product has passed the quality inspection, And paint after the rust-removal is qualified.
3.8.2 The thickness of paint and paint film should meet the design requirements or construction specifications.
3.8.3 Mark the part number at the position specified by the component.
4. Quality standards
4.1 Guaranteed items:
4.1.1 Before the steel structure truss is manufactured and evaluated, the welding and bolt quality assessment shall be carried out firstly, it has to conform the standard specifications.
4.1.2 The variety, specification, model and quality of steel must meet the design requirements and relevant standards.
4.1.3 The cut surface of the steel must be free from cracks, slag delamination and defects of more than 1 mm.
4.2 Basic items:
4.2.1 The surface of the component has no obvious concave surface and damage, and the scratch depth is not more than 0.5 mm. Welds, spatters, and burrs should be cleaned up.
4.2.2 The bolt hole is smooth and has no burr. The vertical deviation of the hole wall is not more than 2% of the thickness of the plate, and the roundness deviation of the hole is not more than 1% of the thickness of the plate.
4.3 Allowable deviation item as below sheet
| No. | Item | Allowable deviation(mm) | Inspection method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The outermost two holes of the roof truss, or the most outer distance of support surface at both ends | L≦24m | +3; -7 | Inspected with steel ruler |
| L>24m | ||||
| 2 | Roof truss mid-height | +10 | ||
| 3 | Roof truss cross mid-degree | Arch lifting is not required in the design | +10; -5 | Inspected with bracing wire and steel ruler |
| Arch lifting required in the design | ±L/5000 | |||
| 4 | Bending of adjacent inter-section chords | L/1000 | ||
| 5 | Connection spacing of fixed purlin | ±5 | Inspected with steel ruler | |
| 6 | Distance from Support surface to the first mounting hole | ±1 | ||
| 7 | Node rod axis staggered | 3 | Inspected with steel ruler after drawing the line | |
Note: L is the length of the roof truss: l is the distance of the chord at the adjacent node.
5. Finished product protection
5.1 When stacking components, the ground must be leveled to avoid uneven force on the fulcrum. The pylons and fulcrums should be reasonable; it should be placed vertically to prevent downward deflection or distortion due to poor side stiffness.
5.2 Steel structural members shall be coated with anti-rust primer and the number shall not be damaged.
6. Quality issues that should be noted
6.1 Components transportation and stacking deformation; when transporting and stacking, the padding is unreasonable, the upper and lower slabs are not on a vertical line, or the deformation is caused by site subsidence and others. If deformation occurs, correct it with a jack, oxyacetylene flame or other tools.
6.2 Distortion of components: When assembling, the steel at the joint is not anastomosed. The gap between the joint steel and the gusset plate is greater than 3mm. It should be corrected. When assembling, clamp with clamps. Long members should be pulled through the wire. After the requirements are met, fix with spot welding. When the long member is turned over, it may be deformed due to insufficient rigidity. In this case, temporary reinforcement shall be carried out in advance.
6.3 Arching does not meet the requirements: When assembling steel roof trusses, the angle of assembly points should be strictly checked, and measures should be taken to eliminate the influence of welding shrinkage and control to avoid cumulative errors.
6.4 Welding deformation: Reasonable welding sequence and welding process (including welding current, speed, direction, etc.) or clamp and tire fixture shall be used to fix the components and then weld to prevent warping deformation after welding.
6.5 Span is not accurate; production, hoisting, inspection should adopts the steel ruler with uniform accuracy, The dimensions of components should be inspected strictly and not allowed to exceed the allowable deviation.
7. Quality record
This process standard shall have the following quality records:
7.1 Quality certificate and test report of steel, connection materials, and coating materials.
7.2 Steel component factory certificate.
7.3 Acceptance records of major components.
7.4 Design change and technology handles negotiation record.
7.5 Ultrasonic flaw detection report of weld seam, test report of anti-slip coefficient of friction surface and coating inspection record.
7.6 Component shipping and packing list.